Please check our Instructions to Authors and send your manuscripts to nifs.journal@gmail.com.
EXTENDED Deadline for submissions: 12 October 2025.
Project:DMEU/Обобщени мрежи
Изследване на възможностите
за използване на Data Mining за управление на процеси в електронен университет
Data Mining in Electronic University
(DMEU) |
Обобщени мрежи, ОМ (Generalized nets, GNs) са средство за конструиране на адаптивни, гъвкави и структурирани модели на комплексни системи, в които протичат паралелни във времето процеси и са изградени от множество взаимодействащи си компоненти. Обобщените мрежи представляват значително разширение и обобщение на понятието мрежи на Петри, както и на други разширения и модификации на мрежи на Петри.
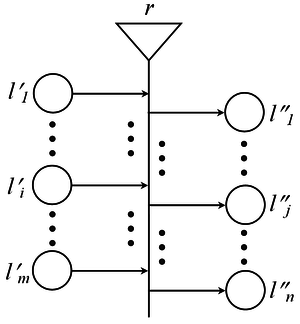
Обобщената мрежа е изградена от преходи (Transitions). Преходът в контекста на обобщените мрежи е обект от статичната структура на мрежата, който съдържа условията за преминаването на ядра (Token) от входните в изходните му позиции (Places), след като преходът се е активирал.
От позиция или в позиция на прехода може да излиза или съответно да влиза не повече от една дъга. Позиция, от която излиза дъга се нарича входна за прехода, а позиция, в която влиза дъга се нарича изходна за прехода. Всеки преход в ОМ има поне една входна и поне една изходна позиция. Входна позиция, в която не влиза дъга се нарича вход на мрежата, а изходна позиция, от която не излиза дъга – изход на мрежата. В позициите може да има ядра. Те се преместват от входните към съответните изходни позиции на преходите. Когато настъпи определения за прехода момент от време, и във входните позиции има достатъчен брой ядра, то ядрата от входните позиции придобиват възможност да се придвижат до изходните позиции. Този процес се нарича активиране на прехода. В началото ядрата, които постъпват в мрежата през входните й позиции имат т.нар. начални характеристики. При всяко преминаване през преход в мрежата те получават нови характеристики и така всяко ядро в мрежата е уникално и има своя история. Всяка позиция има свой капацитет.
Формално описание на преход
Преходът Z в ОМ се представя като наредена последователност от седем компоненти:
където:
- [math]\displaystyle{ L' }[/math] са крайно непразно множество от входните позиции на прехода.
- [math]\displaystyle{ L'' }[/math] са крайно непразно множество от изходните позиции на прехода.
- [math]\displaystyle{ t_1 }[/math] е момент време на активиране на прехода.
- [math]\displaystyle{ t_2 }[/math] задава продължителността на активното състояние на прехода.
- [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math] е условие на прехода. Представлява индексирана матрица от вида:
- [math]\displaystyle{ r = \begin{array}{c|c c c c c} & l''_1 & ... & l''_j & ... & l''_n \\ \hline l'_1 & & & & & \\ ... & & & & & \\ l'_i & & & r_{i,j} & & \\ ... & & & & & \\ l'_m & & & & & \\ \end{array} }[/math]
- където [math]\displaystyle{ r_{i,j} }[/math] са предикати, [math]\displaystyle{ 1 \le i \le m, 1 \le j \le n }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ M }[/math] задава капацитетите на дъгите. Представлява индексирана матрица от вида:
- [math]\displaystyle{ M = \begin{array}{c|c c c c c} & l''_1 & ... & l''_j & ... & l''_n \\ \hline l'_1 & & & & & \\ ... & & & & & \\ l'_i & & & M_{i,j} & & \\ ... & & & & & \\ l'_m & & & & & \\ \end{array} }[/math]
- където [math]\displaystyle{ M_{i,j} \ge 0 }[/math] са естествени числа и [math]\displaystyle{ \infty }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ 1 \le i \le m, 1 \le j \le n }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Box }[/math] се нарича тип на прехода и представлява булев израз. Ако стойността му е “true” съответният преход може да се активира, а ако е “false” - не. В него участват идентификаторите на всички входни позиции на прехода, свързани с логическите операции "и" [math]\displaystyle{ \land }[/math] и "или" [math]\displaystyle{ \lor }[/math]:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \land(l_{i_1}, l_{i_2},...,l_{i_u}) }[/math] - във всяка входна позиция [math]\displaystyle{ l_{i_1}, l_{i_2},...,l_{i_u} }[/math] трябва да има най-малко по едно ядро,
- [math]\displaystyle{ \lor(l_{i_1}, l_{i_2},...,l_{i_u}) }[/math] - най-малко в една от входните позиции [math]\displaystyle{ l_{i_1}, l_{i_2},...,l_{i_u} }[/math] трябва да има най-малко едно ядро.
Формално описание на Обобщена мрежа
Наредената четворка:
се нарича обобщена мрежа, ако:
- 1. Static structure
- [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] is a set of transitions (see the formal definition of a transition)
- [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{A} }[/math] is a function giving the priorities of the transitions, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{A} : A \rightarrow N }[/math] where N = {0, 1, 2, ...} ∪ {∞}
- [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{L} }[/math] is a function giving the priorities of the places, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{L} : L \rightarrow N }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math] is a function giving the place capacities, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ c : L \rightarrow N }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math] is a function giving the truth value of the predicates. In the basic case, it may obtain values "true" (1) and "false" (0). In fuzzy generalized nets its domain is the [0;1] interval (see fuzzy set) and in the intuitionistic fuzzy generalized nets its domain is the set [0;1]×[0;1] (see intuitionistic fuzzy set).
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_{1} }[/math] is a function giving the next time moment when a given transition will be fired (will become active). Hence, [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_{1}(t) = t' }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ t, t' \in [T, T+t^*]; t \le t' }[/math]. The value of this function is being recalculated in the moment when the transition's active state ceases.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_{2} }[/math] is a function giving the duration of the transition's active state. Hence, [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_{2}(t) = t' }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ t, t' \in [T, T+t^*]; t' \ge 0 }[/math]. The value of this function is calculated in the moment when the transition's active state begins.
- 2. Dynamic structure
- [math]\displaystyle{ K }[/math] is the set of tokens of the generalized net. In certain cases it is more convenient to denote this set as [math]\displaystyle{ K = \bigcup_{l \in Q^I} K_{l} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ K_{l} }[/math] is the set of all GN tokens which are waiting to enter place [math]\displaystyle{ l }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Q^I }[/math] is the set of all input places in the net.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_K }[/math] is a function giving the priorities of the tokens, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{K} : K \rightarrow N }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_K }[/math] is a function giving the moment of time when a given token may enter the GN, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_K (\alpha)=t }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \in K, t \in [T; T+t^*] }[/math]
- 3. Time
- [math]\displaystyle{ T }[/math] is the moment of time when the generalized net starts functioning. This moment is determined according to a fixed global timescale.
- [math]\displaystyle{ t^0 }[/math] is the elementary time step of the fixed global timescale (the interval with which time increments in the timescale).
- [math]\displaystyle{ t^* }[/math] is the total duration of functioning of the net.
- 4. Memory
- [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is the set of initial characteristics, which tokens may exhibit when they enter the net for first.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Phi }[/math] is a characteristic function, which assigns a new characteristic to each token when it makes the transfer from an input to an output place of a given transition.
- [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math] is a function giving the maximal number of characteristics, which a given token may obtain during its movement throughout the net, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ b : K \rightarrow N }[/math]. In general, [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math] may possess four different values: 0, 1, [math]\displaystyle{ s }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ \infty }[/math] meaning that the token keeps, respectively: none of its characteristics, its last characteristic, its last [math]\displaystyle{ s }[/math] characteristics, or all of its characteristics obtained during its movement in the net.